June 30, 2022 – Dudu EROL
The difficult pace of technological development causes an increase in volume in the aviation sector, and this increase creates a need for change. These growth-driven changes highlight the need for optimization in both air and ground operations, as well as the need for aviation safety-oriented retrofit. The best illustration of this situation is urban air mobility. With the advancement of technology, increasing rapid vertical construction, signal-impressive towers, and so on, the flight safety risks in aviation have increased. Furthermore, as capacity, flight numbers, and urban air mobility increase, modern aviation faces operational, financial, and time challenges. As a solution to this, effective solutions have started to be produced thanks to geospatial-based aviation developed with technology.
GIS tools have the greatest impact in geospatial aviation. While technology is enabling rapid growth in the aviation sector, ensuring the safety and sustainability of that growth is a challenge. GIS integration in geospatial-based aviation has gained importance for airspace planning, the sustainability of technological developments, and potential risk analysis.
GIS (Geographical Information System) is a whole of spatial or location-based data by digitizing and collecting, analyzing, and presenting geographical data and methods. The digital height models provided by GIS offer important outputs in the conceptualization of real data with virtual reality, three-dimensional simulations, and extensive analysis tools. By making various analyses in the fields of high urban structures and urbanization, access restrictions, land use restrictions, noise pollution, and aviation safety risks, it provides a basis for more efficient aviation studies integrated with technology.
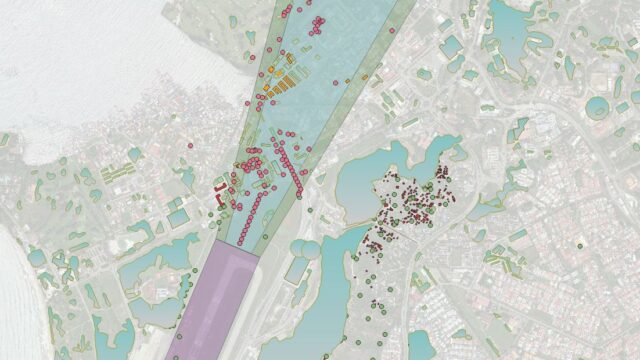
One of the most important examples of GIS in addressing this comprehensive development and the challenges it creates or will create in the modern aviation sector is more advanced airspace modeling tools with geographical information such as rapid urbanization around the airport and changing land use and building heights. These 2D and 3D analyses provide a general framework for airspace and airport perimeter in air/ground operations while providing benefits such as revealing safety risks in landing-take-off corridors, obstacle analysis, and optimization of flight routes.
All this technology-driven growth reveals the need for change and renewal in the data used in airspace construction and landing-takeoff operations, which will create a risk to air operations safety. The digital production of this data for sustainable analysis and renewal is becoming an important point. GIS has become an undeniable importance in the digital creation of this electronic terrain and obstacle data (ETOD) at airports. The ETOD database, which contains geolocation information analyzes created with GIS tools, can also be used as an important database in possible hazard and risk analysis. While this database facilitates the efficiency of airspace, flight safety minimizes the risks to be experienced. In addition to all these, the analysis to be made by integrating the spatial distribution of aviation accidents with these data can present us with risky spatial hotspot areas.
As a result of this,
The advancement of geospatial-based aviation studies in modern aviation also allows for more efficient operation management and an increase in situational awareness in the industry. GIS has begun to keep up with the speed and development of technology in the aviation industry, taking an effective place in the foundations of sustainable development, thanks to the wide-ranging analysis tools and analysis possibilities that are available for development.